Beau Productions Historical Website



President Barack Obama
Slideshow
Listen to BARACK OBAMA - Highlights
while viewing the slide show.
Please be patient - 210 Photos loading
Barack Obama A People's PresidentWhen Barack Obama was elected president in 2008, he became the first African American to hold the office. The framers of the Constitution always hoped that our leadership would not be limited to Americans of wealth or family connections. Subject to the prejudices of their time-many of them owned slaves-most would not have foreseen an African American president. Obama's father, Barack Sr., a Kenyan economist, met his mother, Stanley Ann Dunham, when both were students in Hawaii, where Barack was born on August 4, 1961. They later divorced, and Barack's mother married a man from Indonesia, where he spent his early childhood. Before fifth grade, he returned to Honolulu to live with his maternal grandparents and attend Punahou School on scholarship. In his memoir Dreams from My Father (1995), Obama describes the complexities of discovering his identity in adolescence. After two years at Occidental College in Los Angeles, he transferred to Columbia University, where he studied political science and international relations. Following graduation in 1983, Obama worked in New York City, then became a community organizer on the South Side of Chicago, coordinating with churches to improve housing conditions and set up job-training programs in a community hit hard by steel mill closures. In 1988, he went to Harvard Law School, where he attracted national attention as the first African American president of the Harvard Law Review. Returning to Chicago, he joined a small law firm specializing in civil rights. In 1992, Obama married Michelle Robinson, a lawyer who had also excelled at Harvard Law. Their daughters, Malia and Sasha, were born in 1998 and 2001, respectively. Obama was elected to the Illinois Senate in 1996, and then to the U.S. Senate in 2004. At the Democratic National Convention that summer, he delivered a much acclaimed keynote address. Some pundits instantly pronounced him a future president, but most did not expect it to happen for some time. Nevertheless, in 2008 he was elected over Arizona Senator John McCain by 365 to 173 electoral votes. As an incoming president, Obama faced many challenges-an economic collapse, wars in Iraq and Afghanistan, and the continuing menace of terrorism. Inaugurated before an estimated crowd of 1.8 million people, Obama proposed unprecedented federal spending to revive the economy and also hoped to renew America's stature in the world. During his first term he signed three signature bills: an omnibus bill to stimulate the economy, legislation making health care more accessible and affordable, and legislation reforming the nation's financial institutions. Obama also pressed for a fair pay act for women, financial reform legislation, and efforts for consumer protection. In 2009, Obama became the fourth president to receive the Nobel Peace Prize. In 2012, he was reelected over former Massachusetts Governor Mitt Romney by 332 to 206 electoral votes. The Middle East remained a key foreign policy challenge. Obama had overseen the killing of Osama bin Laden, but a new self-proclaimed Islamic State arose during a civil war in Syria and began inciting terrorist attacks. Obama sought to manage a hostile Iran with a treaty that hindered its development of nuclear weapons. The Obama administration also adopted a climate change agreement signed by 195 nations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and slow global warming. In the last year of his second term, Obama spoke at two events that clearly moved him, the 50th anniversary of the civil rights march from Selma to Montgomery, and the dedication of the National Museum of African American History and Culture. "Our union is not yet perfect, but we are getting closer," he said in Selma. "And that's why we celebrate," he told those attending the museum opening in Washington, "mindful that our work is not yet done." The Presidential biographies on WhiteHouse.gov are from "The Presidents of the United States of America," by Frank Freidel and Hugh Sidey. |
Barack Obama on Social Security - Tap the video for sound
Beau Productions (BP) Historical Trading Card
Collectable Barack Obama - "Yes We Can" Novelty Trading Card
If you are interested in our Barack Obama - Historical Novelty Trading Card (same as baseball cards) as shown below you may purchase on eBay for as little as $8.00 or less.
Click or tap images if interested
FRONT AND BACK OF CARD


Click the images above to get your Obama "Yes We Can" Historical Novelty Trading Card
Beau Productions also created two other Barack Obama Historical Trading Cards highlighting
Obama's Basketball and Golf history. Visit Obama's Golf and Basketball sites below.
Beau Productions (BP) Historical Trading Cards
Collectable Barack Obama - "That's What I Do" Novelty Trading Card
If you are interested in our Barack Obama - Novelty Trading Card (same as baseball cards) as shown below you may purchase on eBay for as little as $8.00 or less.
Click or tap images if interested


Click the images above to get your Obama "That's What I Do" Novelty Trading Card
Also check out the following Historical Obama Cards.
Collectable Barack Obama - Novelty Golf Trading Card
If you are interested in our Barack Obama - Golf Novelty Trading Card (same as baseball cards)as shown below you may purchase on eBay for as little as $8.00 or less.
Click or tap images if interested
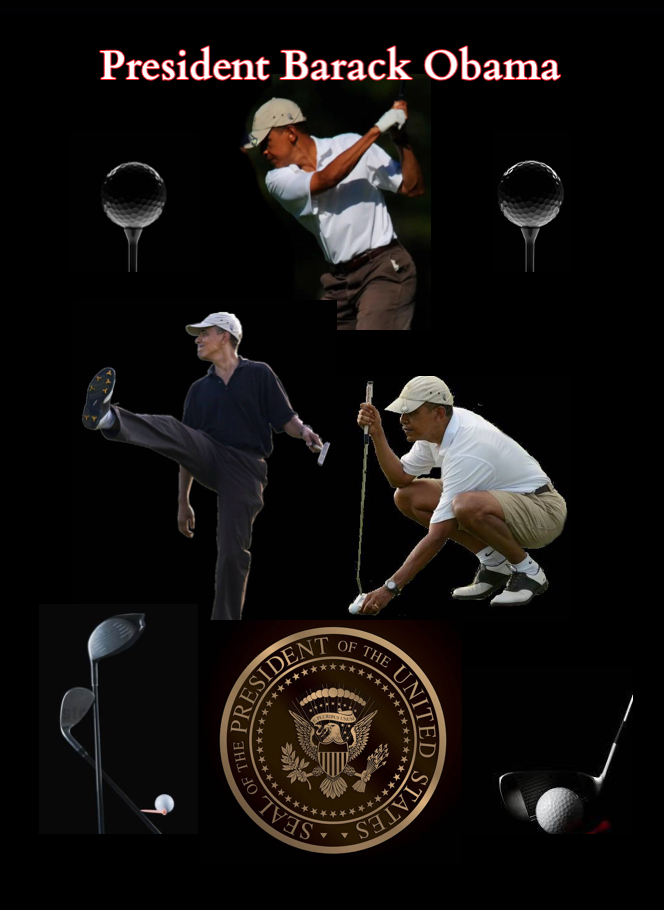


Click the images above to get your Obama Golf Novelty Trading Cards
You can purchase all three cards for only $12.00 - Click Here






Visit President Obama's Basketball Slideshow

Visit President Obama's Golf Slideshow
Copyright All Rights Reserved Beau Productions LLC 2008
Top

All Beau Productions Websites are virus free and protected. Guaranteed!
Beau Productions Historical Website